Visual thinking & understanding in BA / RE / ARCH practices used in industry product development
The concept of visual management and visual feedback is one of the pillars in Lean Product development for communication of status, progress, prognosis, and planning, e.g. tracking of work identified, ongoing and done in the development teams via kanban-like boards as well as the progress according to existing plan, expectations and what is actually delivered.
The leaders of the development teams are more interested in the use of resources and the amount of work to be done, so future work can be planned accordingly. The downstream stakeholders like sales, manufacturing, marketing etc. also need to SEE how the projects are doing so they can plan and be ready at the right time.
The knowledge needed and the representations used, are pragmatic and efficient for management and planning, and the focus is NOT on the visual thinking and understanding of what shall be done. Only the management and control aspects of the development are considered.
In the BA/RE practice you often get advice to use X or Y or Z but no direction on WHICH representation to use and no focus on reasoning regarding the effect on this choice for downstream development. The often individual decisions are suspiciously sub-optimal with no supporting knowledge of consequence of the specific Knowledge Representational choice as it will most likely affect the way we see things, think and are able to invent… but most importantly the ignorance of what we do NOT see and what has been lost in the knowledge transformation along the way —“the Software Engineering “Chinese whispers game”(” Telephone-, Gossip game”, “viskleken”) aka “the agile guessing game”…

The essence of the game is that “Whispered messages” are passed around the room and the version which comes back to the starting point bare no relation to the original message. This phenomenon of “whispering” can also be extended to “not really understanding” in a more general sense to describe every day “mis-telling” of stories and misunderstanding of knowledge in any setting or form, when only using talk and sloppy writing are used as for knowledge communication. In fact, the sheer existence of this “whispering effect” is one of the reasons why LEAN and AGILE will never really work in Software Engineering without a sincere and focused knowledge representation for thinking and understanding!
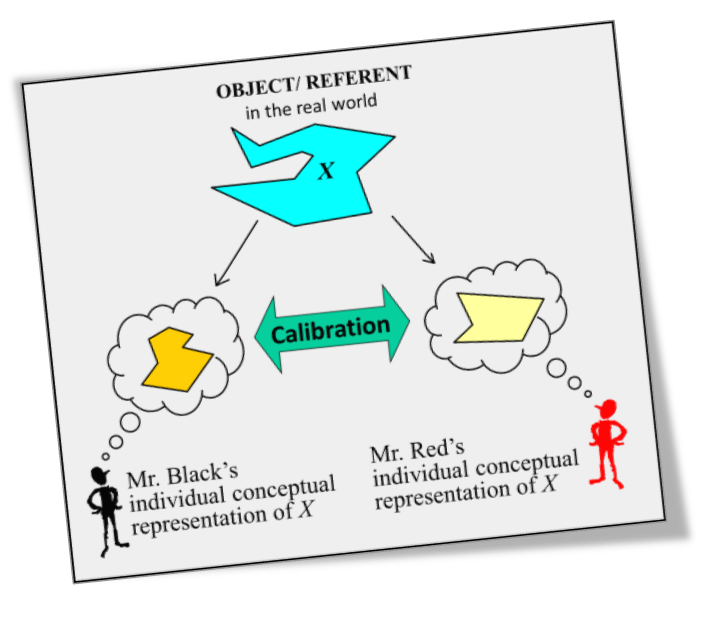
We are lacking a focus on HOW we make the decision between different Visual Knowledge representations and the effect of our choices both at the same level regarding knowledge, understanding, innovation, and creativity, but also the downstream understanding of WHAT is communicated and what is NOT represented at all.
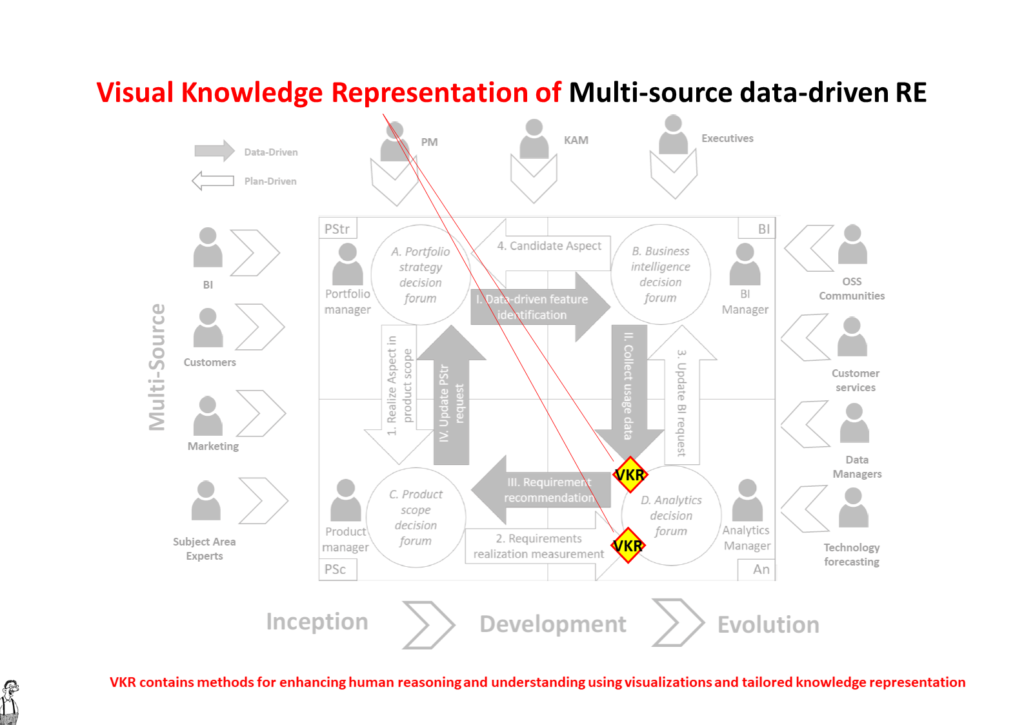
Most models are not explicitly showing the Visual Knowledge Representation, but can easily be enhanced by a VKR component. For example the VKR decision point in the MSDDRE model
And by the way, this is my research domain. Do you want a draft title? OK here we go:
“Formal & informal Visual Knowledge Representation used for knowledge transfer in Requirements Engineering, Business Analysis and Software Architecture
– evaluation of real usage in industry, choice of representation and diagram narratives to identify difficulties and errors in thinking and how to find the Best Possible, Good-enough and Visual Knowledge Representation with focus on the properties required for formal modeling in practice”

Stefan Eekenulv
Senior konsult på Castra
Stefan är passionerad för krav, verksamhetsanalys och visualisering av kunskap för att få det att funka i verkligheten. En annan passion är MonoSki och god öl. Stefan driver industriforskning kring pragmatic knowledge representation tillsammans med Blekinge Tekniska Högskola och Castra. Han håller även i kurser inom IREB, läs mer här.